Chocolate has evolved dramatically over the last decade. What was once a simple indulgence has now become a complex category influenced by bean-to-bar craftsmanship, sustainable sourcing, functional nutrition, and clean-label consumerism. As a result, reading a chocolate label in 2026 is not as straightforward as it used to be.
This guide cuts through the noise—breaking down every part of a chocolate label so you can make informed decisions about quality, nutritional value, ethics, and functionality. Whether you’re buying premium dark chocolate, bean-to-bar craft bars, or functional chocolates enhanced with botanicals, this guide will help you read labels like an expert.
Three global trends have transformed the way consumers evaluate chocolate:
1. The rise of clean-label expectations
Shoppers now look for fewer, more natural ingredients, minimal additives, and transparent sourcing.
2. Growth of functional chocolates
Ingredients like maca, spirulina, L-citrulline, and plant proteins have become mainstream additions. Understanding what they do—and how they’re regulated—is crucial.
3. Stronger focus on sustainability and ethics
Certifications and origin disclosures matter more than ever.
Decoding the Cacao Percentage (%)
The cacao percentage (55%, 70%, 85%, etc.) represents the total amount of cocoa mass, cocoa butter, and cocoa solids. It does not guarantee bean quality, ethical sourcing, or flavor excellence.
What different percentages generally mean:
- 50–60%: balanced sweetness
- 60–75%: classic dark chocolate with lower sugar
- 75–85%: bold and complex flavor
- 85–100%: very intense, for purists
- Higher percentage ≠ automatically healthier. It’s only one piece of the puzzle.
Ingredient List — The Most Important Part of the Label
The ingredient list reveals everything you need to know about chocolate quality. Fewer, recognizable ingredients typically indicate cleaner, purer chocolate.
Green-Flag Ingredients (Good Signs)
- Cocoa mass / cacao nibs: foundation of real chocolate
- Cocoa butter: natural cocoa fat; ensures premium texture
- Natural sweeteners (jaggery, coconut sugar): less processed alternatives
- Plant proteins (e.g., mung bean protein): functional nutrition
- Botanicals (maca, spirulina): natural functional additions
Craft and functional brands like Kalories often use natural sweeteners and botanicals while maintaining clean-label principles.
Red-Flag Ingredients (Avoid When Possible)
- Hydrogenated vegetable fats: cheap replacement for cocoa butter
- Artificial flavors (especially vanillin): used to mask poor bean quality
- Excessive emulsifiers (PGPR high on the list): heavy industrial processing
- Corn syrup / glucose syrup: highly processed sweeteners
When artificial flavors appear before cocoa mass, it’s almost always low-quality chocolate.
Emulsifiers, Additives & Stabilizers
Emulsifiers are common in chocolate manufacturing but must be assessed carefully.
Common emulsifiers you’ll see:
- Soy lecithin
- Sunflower lecithin
- PGPR (Polyglycerol Polyricinoleate)
What’s acceptable?
- Lecithins used sparingly are fine.
- PGPR high on the list signals heavy processing.
Sugars & Sweeteners — What Really Matters
Sugar affects taste, health, and quality.
Types of sweeteners you’ll see in 2026:
- Jaggery: natural, less processed
- Coconut sugar: lower GI
- Raw cane sugar: acceptable
- Refined sugar: common but lacks nutrients
- Sugar alcohols (maltitol, erythritol): may cause digestive discomfort
- High-fructose syrups: best avoided
Premium brands increasingly shift toward natural sugars.
Functional Ingredients — The New Frontier of Chocolate
Functional chocolates have become a major global trend. You’ll often see ingredients such as:
- Maca root: traditionally used for vitality
- Spirulina blue algae: antioxidant-rich, nutrient dense
- L-Citrulline: supports performance and blood flow
- Mung bean protein: clean plant protein source
- Botanical extracts (e.g., epimedium): cultural wellness uses
Important consumer note:
Claims must follow regulatory guidelines (FSSAI, FDA, EFSA). Look for modest phrases like:
- “supports energy levels”
- “may aid performance”
- “traditionally used for…”
Avoid products that promise unrealistic results.
Certifications to Look For in 2026
Certifications validate transparency and sustainability.
Common chocolate certifications:
- Fair Trade
- Rainforest Alliance
- USDA Organic / India Organic
- Non-GMO Project
- Bean-to-Bar or Single-Origin disclosures
Not all premium chocolates have every certification, but credible brands are transparent about sourcing and processing.
Country of Origin — Why It Matters
Country or region of origin influences flavor, ethics, and traceability.
General flavor signatures:
- Peru: floral, fruity
- Ghana: rich and classic
- Ecuador: aromatic, nutty
- India (Kerala, Andhra, Karnataka): bold, emerging terroirs
Single-origin bars often deliver more character and transparency.
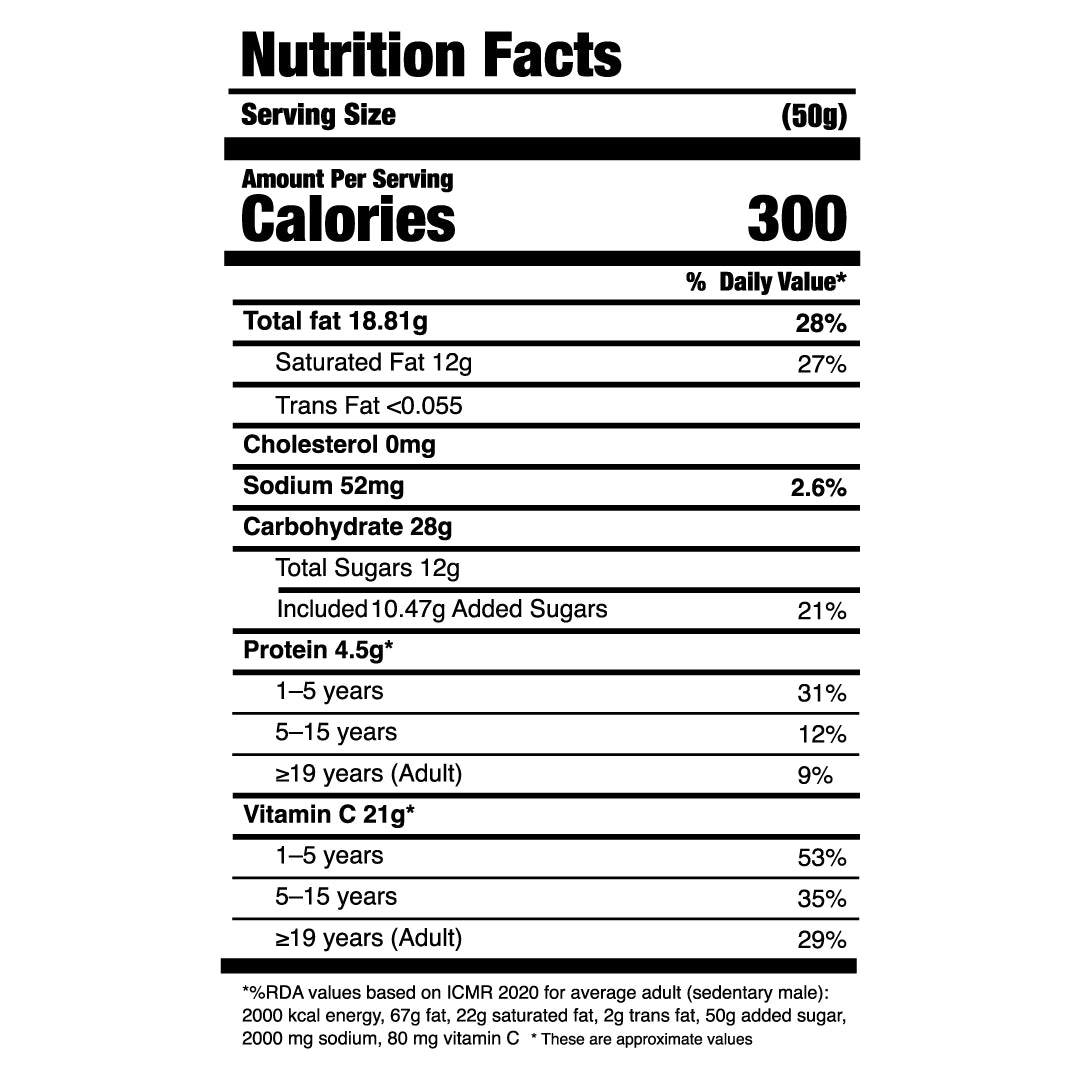
Nutrition Facts — What to Check
- Serving size: can be manipulated
- Total sugars: compare with cacao %
- Protein: higher in functional chocolates
- Fat composition: cocoa butter should dominate
- Fibre: dark chocolate is naturally higher
Choosing the Right Chocolate for Your Goals
For Energy:
Look for natural carbs, plant proteins, maca, L-citrulline, spirulina.
For Indulgence:
Choose 55–75% cacao with rich cocoa-butter texture.
For Clean Label:
Minimal ingredients. No artificial flavors or palm oils.
For Mood:
55%+ cacao with simple ingredients.
10-Second Chocolate Label Checklist
- Check cacao % (ideal: 55–85%).
- Cocoa mass should be the first ingredient.
- Avoid palm oil and hydrogenated fats.
- Avoid artificial flavors like vanillin.
- Prefer jaggery or coconut sugar.
- Look for minimal emulsifiers.
- Check sugars per serving.
- Look for meaningful certifications.
- Evaluate functional ingredients carefully.
- Choose brands with transparent sourcing stories.
Conclusion — Becoming a More Informed Chocolate Consumer
Understanding how to read a chocolate label empowers you to choose products that are not only delicious but also transparent, ethical, and aligned with your nutrition or lifestyle goals.
Premium and functional chocolate brands like we at Kalories prove that clean ingredients, natural sweeteners, and powerful functional botanicals can come together beautifully—without ever compromising on flavor.
In 2026, the best chocolate isn’t just tasty. It’s transparent, functional, and honestly crafted.